Hackers are targeting other hackers with a fraudulent OnlyFans tool that claims to help steal accounts but instead infects cybercriminals with the Lumma Stealer, an information-stealing malware.
The operation, discovered by Veriti Research, serves as a characteristic example of the blurred lines between being a predator or prey in the world of cybercrime, where ironic twists and betrayals are abundant.
“Checking” into a Lumma infection
OnlyFans is a highly popular subscription-based adult content platform where creators can earn money from users (called “fans”) who pay for access to their content.
Creators can share videos, images, messages, and live streams with subscribers, who pay either a recurring fee or make one-time payments for exclusive content.
Due to its popularity, OnlyFans accounts often become targets for cybercriminals who try:
- to hijack them to steal fan payments,
- extort the account owner for ransom,
- or leak private photos.
Checker tools are built to validate large sets of stolen login credentials (usernames and passwords), confirming if the details match any OnlyFans accounts and whether they’re still valid.
Without these tools, cybercriminals would have to manually test thousands of credential pairs, a tedious and impractical process that would make the scheme unworkable.
However, these tools are often created by other cybercriminals, leading hackers to trust their safety, which sometimes backfires.
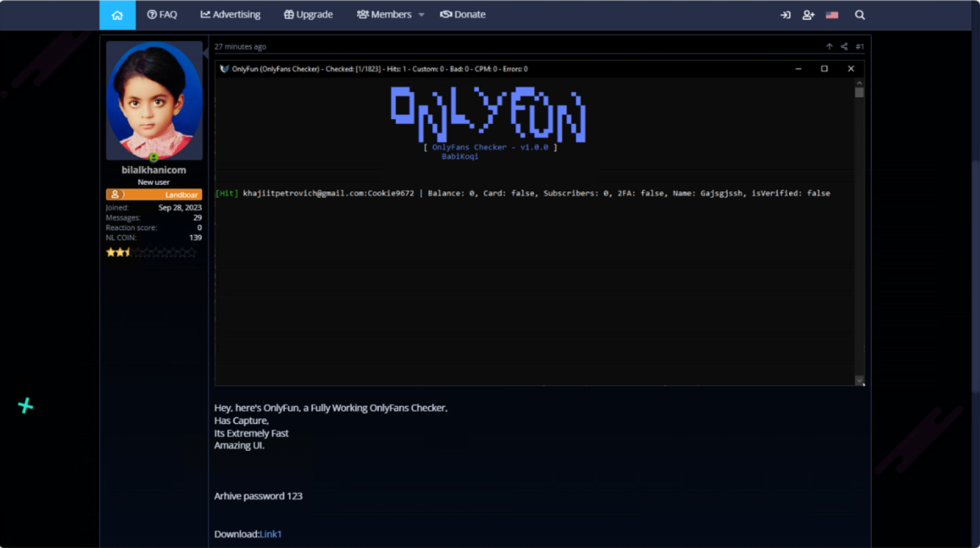
Veriti uncovered a case where an OnlyFans checker tool, claiming to
- verify credentials,
- check account balances,
- confirm payment methods,
- and assess creator privileges,
actually installed the Lumma information-stealing malware.
Threat actor’s checker ad on a hacker forum
Source: Veriti
The payload, named “brtjgjsefd.exe“, is retrieved from a GitHub repository and loaded onto the victim’s computer.
Lumma is an information-stealing malware-as-a-service (MaaS) that has been leased to cybercriminals since 2022 for $250-$1000 per month. It is distributed through various channels such as malvertising, YouTube comments, torrents, and, more recently, GitHub comments.
It is a sophisticated information stealer with advanced evasion techniques and the capability to restore expired Google session tokens. Lumma is primarily known for stealing two-factor authentication codes, cryptocurrency wallets, passwords, cookies and credit card details stored in the victim’s browser and file system.
Lumma also functions as a loader, capable of delivering additional payloads to the compromised system and running PowerShell scripts.
A broader deception operation
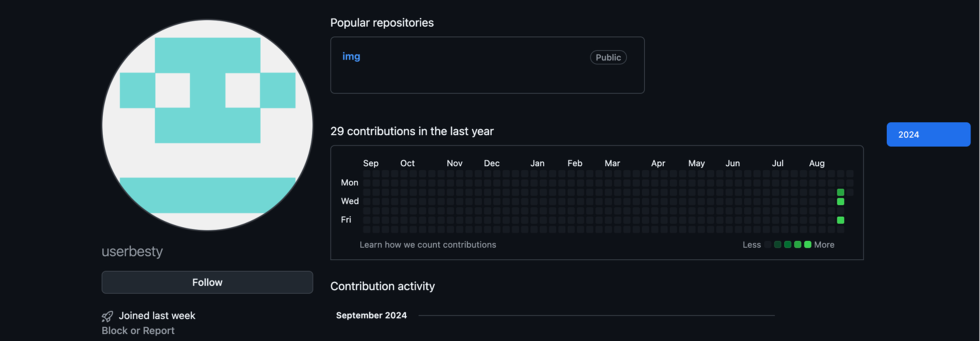
Veriti discovered that when the Lumma Stealer payload is activated, it connects to a GitHub account under the name “UserBesty“, which the cybercriminal behind this campaign uses to host additional malicious payloads.
Malicious GitHub repository
Source: Veriti
The GitHub repository specifically contains executables that mimic checkers for Disney+ accounts, Instagram, and a supposed Mirai botnet builder:
- Disney+ account thieves are baited with “DisneyChecker.exe”
- Instagram hackers are enticed by “InstaCheck.exe”
- Aspiring botnet creators are drawn in with “ccMirai.exe”
Upon further investigation into the malware’s communications, Veriti’s researchers uncovered a set of “.shop” domains functioning as command and control (C2) servers, which send instructions to Lumma and receive exfiltrated data.
This campaign is not the first instance of cybercriminals targeting fellow hackers in malicious attacks.
In March 2022, hackers attacked other hackers using clipboard stealers disguised as cracked RATs and malware-building tools to steal cryptocurrency.
Later that year, a malware developer backdoored their own creation to steal credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, and VPN account data from other cybercriminals.
Source: BleepingComputer, Bill Toulas
Read other news at our blog