Hackers exploited a critical vulnerability and the built-in antivirus feature in Gladinet’s Triofox file-sharing and remote-access platform, enabling them to execute remote code with SYSTEM privileges.
The attackers took advantage of the security issue CVE-2025-12480, which allows them to bypass authentication and access the application’s setup pages.
On August 24, security researchers at Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) uncovered the malicious activity after identifying a threat cluster, internally tracked as UNC6485, that targeted a Triofox server running version 16.4.10317.56372, released on April 3.
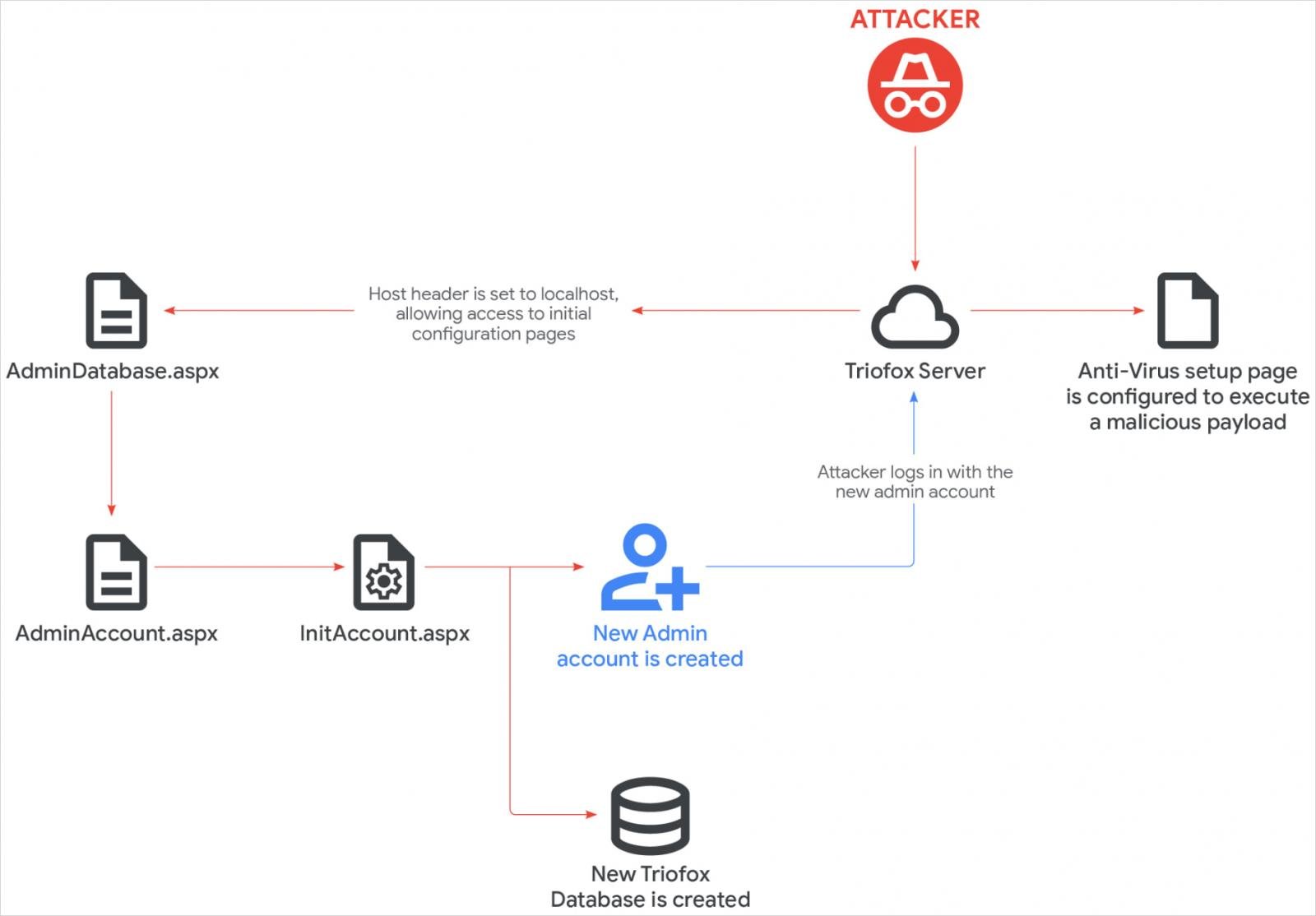
The root cause of CVE-2025-12480 stems from an access control logic gap that grants admin access whenever the application’s request URL host equals “localhost.”
Consequently, attackers can spoof this value through the HTTP Host header, allowing them to completely bypass authentication checks.
Mandiant explains that when administrators fail to configure the optional TrustedHostIp parameter in web.config, the “localhost” validation becomes the only safeguard, leaving default installations fully exposed to unauthenticated access.
To close this security hole, Gladinet released a fix for CVE-2025-12480 in Triofox version 16.7.10368.56560 on July 26. GTIG researchers later confirmed with the vendor that the update successfully addressed the flaw.
Abuse of the Antivirus Feature
Mandiant’s investigation revealed that UNC6485 exploited the vulnerability by sending an HTTP GET request containing “localhost” in the HTTP Referer URL.
“The presence of the localhost host header in a request originating from an external source is highly irregular and typically not expected in legitimate traffic,” the researchers explain.
This maneuver gave the attackers direct access to the AdminDatabase.aspx configuration page, which Triofox launches during the initial setup process.
From there, the attackers used the setup workflow to create a new administrator account named “Cluster Admin.” They then uploaded a malicious script and configured Triofox to use its path as the antivirus scanner location.
GTIG clarifies that “the file configured as the anti-virus scanner location inherits the Triofox parent process account privileges, running under the context of the SYSTEM account,” which allowed the attackers to achieve full code execution.
According to the researchers, the malicious batch file executed a PowerShell Downloader that Retrieved another payload — a Zoho UEMS installer — from an external source.
The UNC6485 attack chain
Source: Google
The attackers then used Zoho UEMS to deploy Zoho Assist and AnyDesk on the Compromised host, Enabling remote access and lateral movement across the network.
To strengthen their Foothold, they also Downloaded and used Plink and PuTTY to establish an SSH tunnel and forward remote traffic to the host’s RDP port (3389).
Post-exploitation activity
Source: Google
The Patches
Although Mandiant confirmed that CVE-2025-12480 was patched in Triofox version 16.7.10368.56560, the firm urges system administrators to apply the latest security update in version 16.10.10408.56683, released on October 14.
Additionally, Mandiant recommends Auditing Administrator accounts and Verifying that Triofox’s Antivirus engine is not Configured to execute Unauthorized scripts or Binaries.
GTIG’s report includes a comprehensive list of indicators of compromise (IoCs) to help defenders detect and prevent these attacks. The full details are also available on VirusTotal.
Finally, in October, Huntress reported that hackers Exploited another Zero-day flaw — a local file Inclusion Vulnerability (CVE-2025-11371) — affecting Gladinet CentreStack and Triofox. This flaw allowed Attackers to access system files without Authentication and led to at least three successful Intrusions before Gladinet fixed it a week later in version 16.10.10408.56683, the latest release.
Source: BleepingComputer, Bill Toulas
Read more at Impreza News